I posted an item on 7 June 2013 on photographing the ISS. As I now have a different camera and lenses and as we have clear skies I decided to do an update.
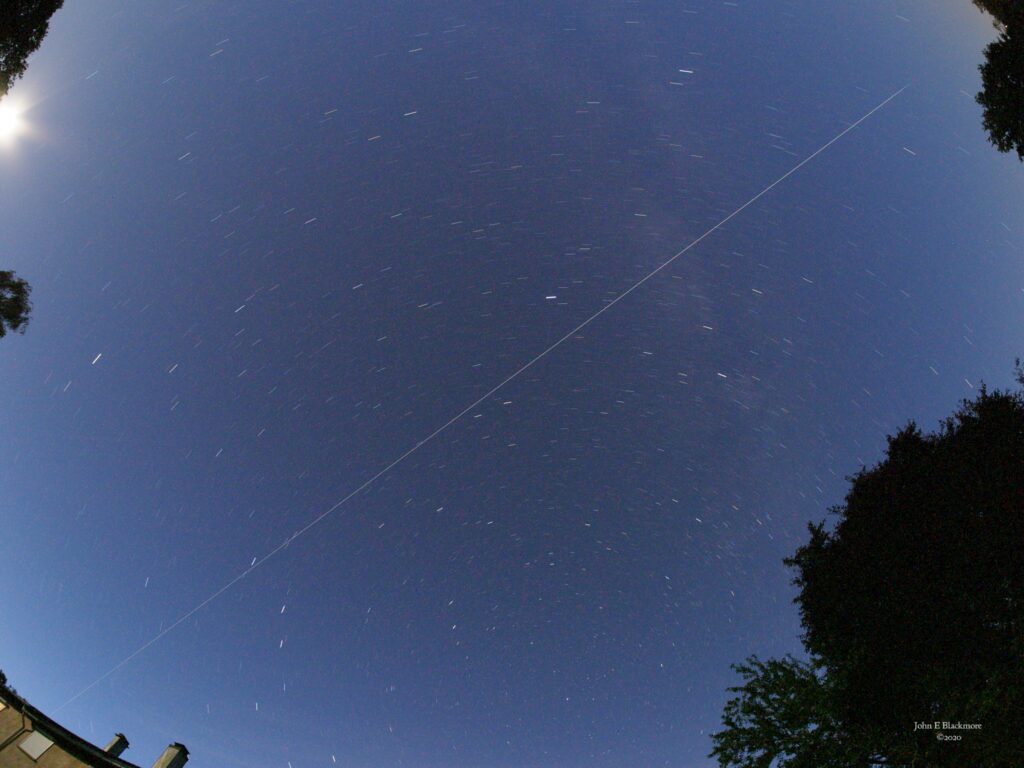
I now use the ISS Detector app on my phone to notify me of upcoming events. At 22:38 on Monday 27 July 2020 there was a possible nearly overhead ISS sighting (max. height 86°, appearing 27° above WNW disappearing 22° above ESE). The first quarter moon was not too bright and not likely to cause problems. So I set my tripod in the field below the farmhouse, in the best position to avoid the farmhouse and surrounding trees blocking the overflight path. I had a 7.5mm Samyang fisheye lens on my camera and set it at an angle to give me the likely full path across the diagonal of the image . With the lens set at f8, I opened the shutter just before the predicted appearance time. The ISS passed over and disappeared from sight just before the end of the path and I then shut the shutter. This is the resulting unedited image:
As I was satisfied with that photograph, the following day I was just out taking some photographs of the moon with a 75-300mm zoom lens (and also attempting some photographs of Jupiter). I’d forgotten about the ISS but suddenly saw it appear above the orchard trees. Rather than trying to take partial path picture, I wondered whether it was possible to just take a snapshot of the ISS itself. I had no idea of exposure settings and had little time so just took a guess at what to use. I loosened the ball and socket mount so I could swivel the camera to track the ISS and set the lens to 75mm in the hope of seeing the ISS through the viewfinder with the wider view. That wasn’t too difficult and I was then able to zoom to 300mm (= 35mm full-frame 600mm) and to track the ISS, pressing the release several times to take photographs. The results were rather mixed, poorly exposed, and showed camera shake but gave me an indication of what might be possible.
So I decided I might be able to do better the next night with some proper preparation. I set the camera exposure to a faster shutter speed and higher ISO and also set the camera to take an automatic succession of photographs to try to reduce the initial movement from pressing the shutter release (at that focal length the camera is very sensitive to the slightest movement). I had to use the release button on the camera as I needed both hands to help track the ISS smoothly so couldn’t easily use my phone as a remote control.
I took over 100 photographs. About 10% have an image that on close inspection is discernible as an object rather than just a white, slightly blurred, blob. I doubt I would be able to get a better photograph with that lens. I would need the camera attached to a telescope which had automated tracking.
This shows one of the full images with the ISS arrowed. I’ve pasted an enlarged version of that faint white dot in the RH corner. The ISS in the image is only 20×16 pixels overall. It was pleasing as I’d not really expected such a positive result.
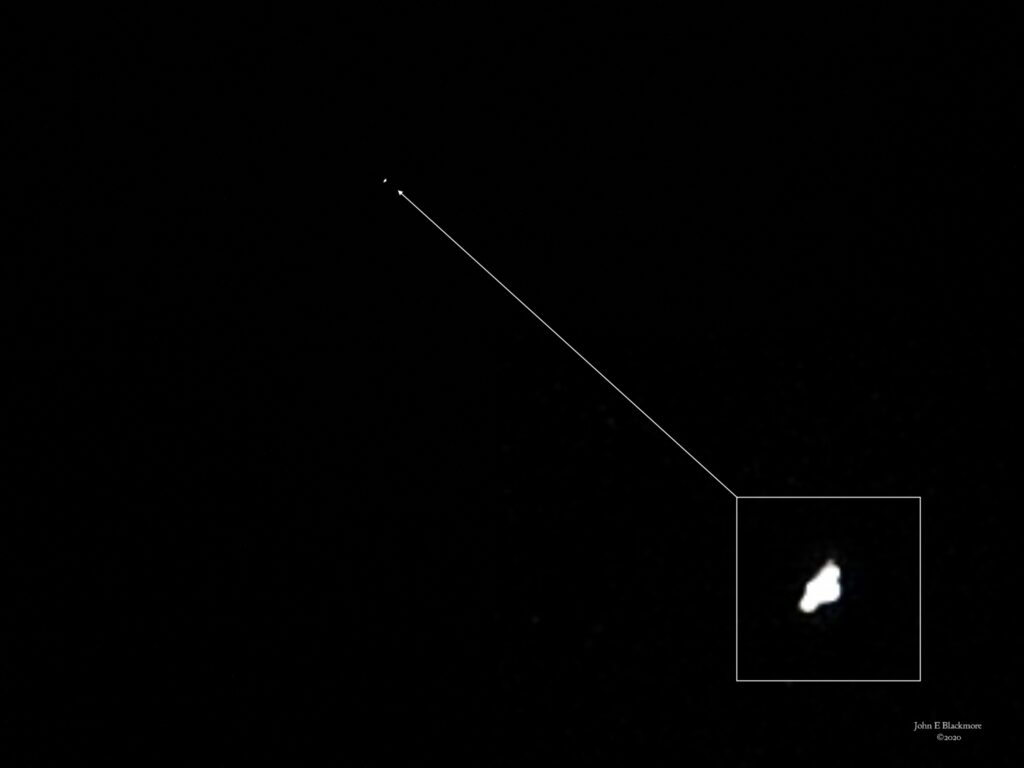

According to http://www.isstracker.com/historical the ISS was at 45.874N 3.008W (over Volvic in Central France) at an altitude of 262.45 miles and travelling at 17,144.65 mph.